Appearance
DOHSBase evaluation of notified classifications
DOHSBase evaluation of notified classifications
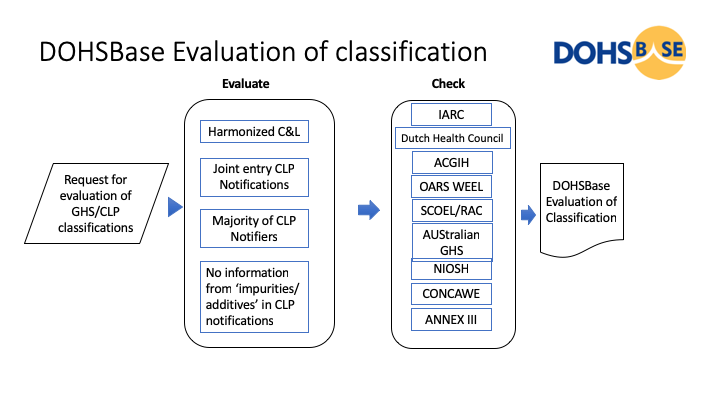
For some substances without a harmonized European classification (CLP), it may be desirable to have a good assessment of a classification. For example, for prioritizing substances or for deriving a company OELV or kick-off value. For these substances it is possible to establish a so-called DOHSBase Self Classification based on data from the substance in the C&L inventory of ECHA or other sources (e.g. IARC and / or the Australian classification). This is done by DOHSBase as consultancy, at the request of customers, by experienced occupational hygienists and toxicologists. DOHSBase has developed a system for this
If the notified classifications in the ECHA database are taken as the starting point, the starting point is 'the greatest common denominator' of the assessments by the notifiers (groups of or individual registrants of the substance in the context of REACH). The following procedure is used.
In DOHSBase Compare the results are displayed in the fields Classification, GHS Hazard Statement Codes and the GHS symbols. See the example below. In addition to the Self Classification (GHS classification, H-sentences), it also indicates how many notifiers have this classification (and the total number of notifiers) and whether there is a group classification (joint entry). The date that the Self Classification was carried out is also mentioned. The H-phrases from the Self Classification are also displayed in the field GHS Hazard Statement Codes. Finally, the GHS symbols associated with the Self Classification are displayed.
