Appearance
Physical State
Physical State
The following definitions are given in the CLP Regulation (1272/2008) defines in Annex I the physical state as follows:
* Gas is a substance which:
(i) at 50 o C has a vapour pressure greater than 300 kPa (absolute); or
(ii) is completely gaseous at 20 o C at a standard pressure of 101,3 kPa;
* Liquid is a substance or mixture which:
(i) at 50 o C has a vapour pressure of not more than 300 kPa (3 bar);
(ii) is not completely gaseous at 20 o C and at a standard pressure of 101,3 kPa; and
(iii) which has a melting point or initial melting point of 20 o C or less at a standard pressure of 101,3 kPa;
* Solid is a substance or mixture which does not meet the definitions of liquid or gas.
in DOHSBase Compare the physical state at 25�C and at normal atmospheric pressure (1 atm, 1013 mbar, 760 mm Hg, 1013 hPa, 101325 Pa) is presented. In general:
- When the Boiling Point is below 15�C this is considered 'gas'; at temperatures between 15�C en 30�C this is considered 'gas or liquid'.
- When the Melting Point is below 15�C this is considered 'liquid'; at temperatures between 15�C en 30�C this is considered 'liquid or solid'.
- When the melting point is greater than 30�C, the substance is a solid.
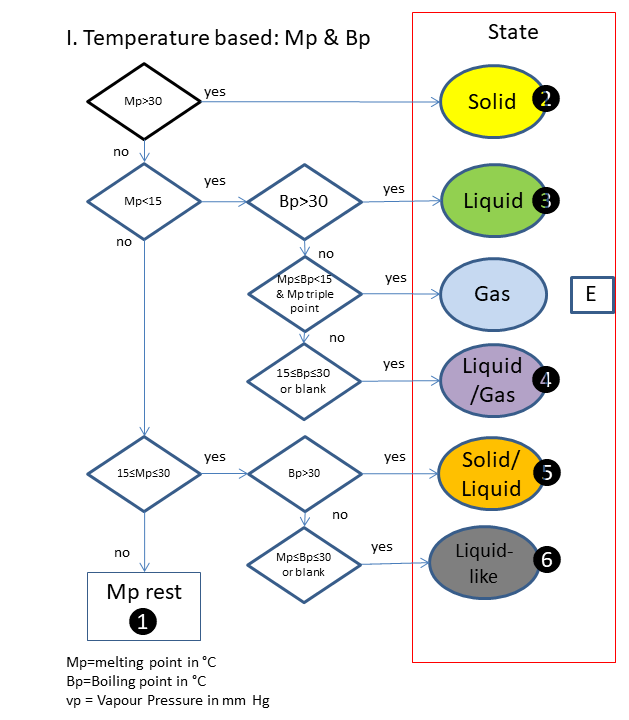
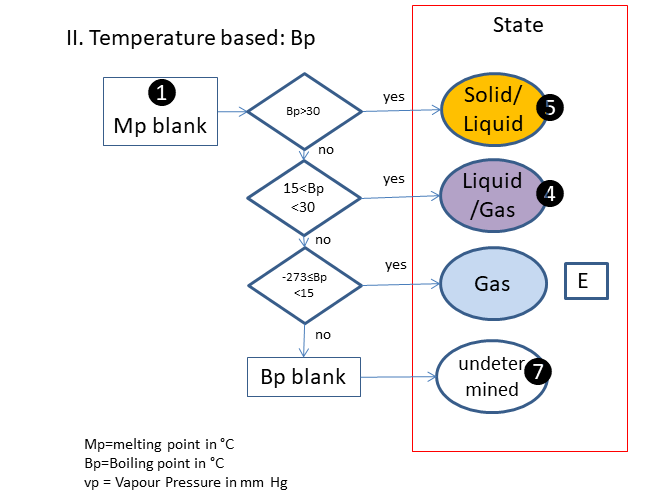
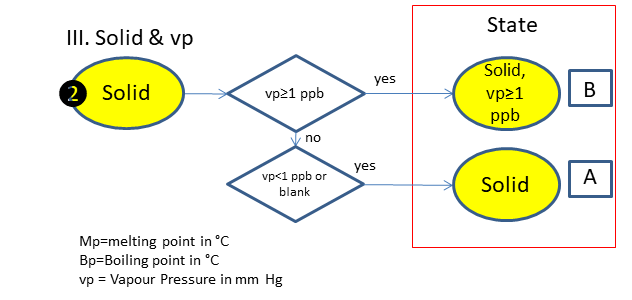
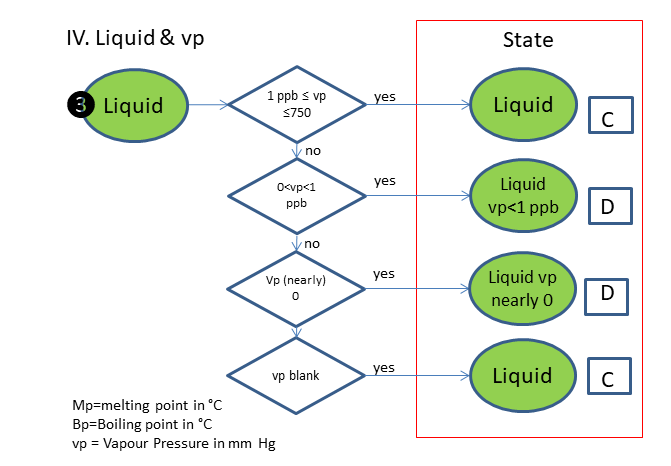
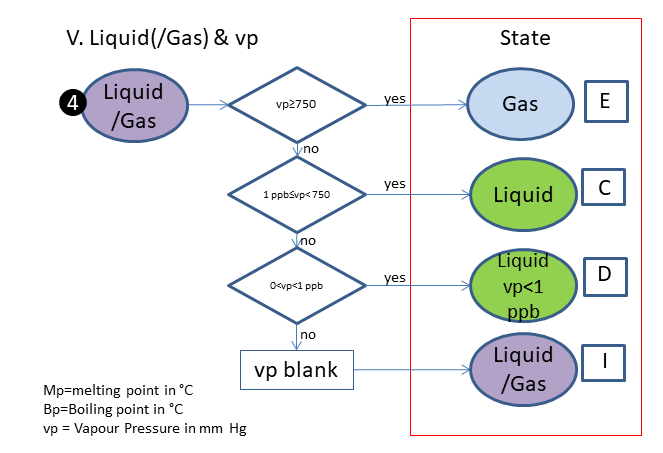
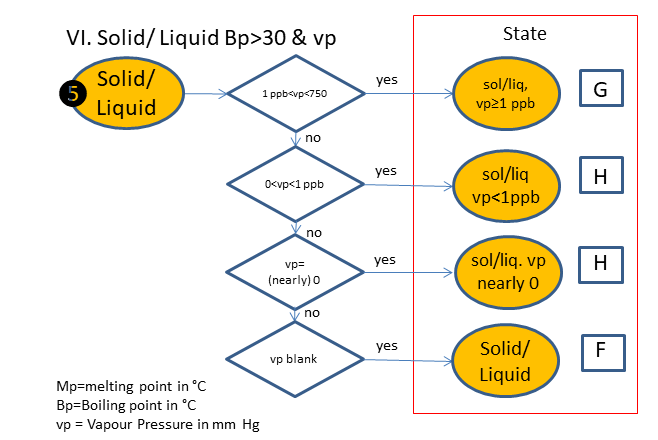
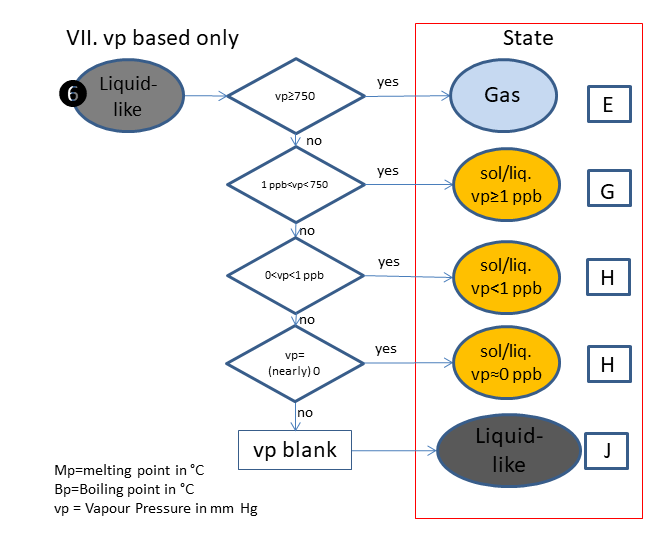
If the physical state is not clear, the following scheme is used (based on melting & boiling point), in which is:
A. Solid
B. Solid, vp>_1 ppb
C. Liquid
D. Liquid, vp<1 ppb
E. Gas
F. Solid/Liquid
G. Solid/Liquid, vp>_1 ppb
H. Solid/Liquid, vp<1 ppb
I. Liquid/Gas
J. Liquid-like
K. Unknown
L. Fibre
M. Varying