Appearance
Kick-off Levels
Kick-off Levels
For substances without defined limit values it is possible to derive so-called Kick-off levels from the assigned Hazard Statements ([H-statements](../03_substance_properties/GHS Hazard Statement Codes.md)) of these substances (see also Scheffers & Wieling, 2005). Kick-off levels are based on the distribution of limit values for substances groups of H-statements ('hazard classes') in several Control Banding systems. Kick-off levels are defined as equal to the 10%-tile lower tolerance limit of the limit values in a hazard class. This means that 90% of the limit values of the substances in a hazard class is higher than the kick-off level for that hazard class. Therefore, the kick-off levels are conservative by nature.
The advantage of a Kick-off level at a technical and economic feasible level, is that the (expensive) procedure to a to establish a formal limit value can be omitted. If the Kick-off level is not technically or economically feasible, then the procedure to establish a more accurate and often higher limit, can still be started (a.o. (animal) experimental or epidemiological studies, with extrapolation factors). The "real" dose-response-based Occupational Hygiene Limit Value of the substance is above this kick-off level with a probability of 90% .
The kick-off levels were originally described in 2005 (based on the comparison with R-phrases) and recalculated in 2014 (based on de comparison with H-statements).
In the Compare Mode the kick-off level of a substance is presented in yellow.
Kick-off levels are not calculated if the physical state is not known, nor with 'fibers'.
In the absence of the physical state, the saturation concentration is used to present a kick-off level in:
- ppm, if the saturation concentration is equal or greater than the kick-off level (Csat >= kick-off level);
- mg/m3, if the saturation concentration is smaller than the kick-off level (Csat < kick-off level).
The following table lists the H-statements associated with each Hazard Class. The table also contains the derived Kick-off level for each Hazard Class. The Kick-off levels for dusts are presented in mg/m3 (a substance gets a kick-off value from the H-statement in the highest Hazard Class). The Kick-off level for gases and vapours are in parts per million (ppm). To convert these to mg/m3 the molecular mass has to be used.
Kick-off levels 2014:
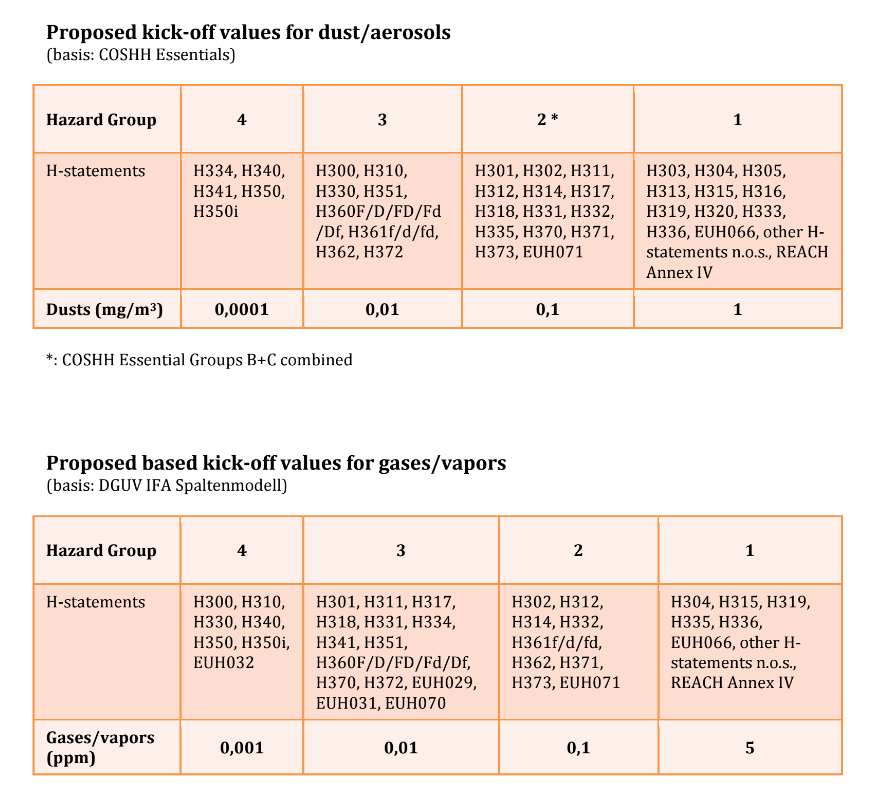
The kick-off levels (only as TWA 8 hours) are based on the study of Scheffers and Wieling, published in 2005 (Journal of Applied Occupational Sciences [Tijdschrift voor toegepaste Arbowetenschap (TtA)] vol. 18, 2005, p. 67-75; in Dutch, with English summary); Click for the reference on the internet). On our website there is more information regarding the kick-off levels:
